How to Do Mozilla Firefox Faster Again!
Have you experienced the SPEEDY FIREFOX browser slowing down or crashing? It's the reason of unwanted plug-ins, extensions, and the browsing data could do the browser speed slow or even crashing.
Well! We'll discuss how to rectify the problems to speeding-up Firefox by disabling plug-ins, extensions and clearing browsing data.
 Plug-in (or plugin) is a piece of software components, which adds specific abilities to an application and commonly used in web browsers to play video, audio, online games, presentations, scanning viruses, display new file types and more.
Plug-in (or plugin) is a piece of software components, which adds specific abilities to an application and commonly used in web browsers to play video, audio, online games, presentations, scanning viruses, display new file types and more.
Plug-in helps Firefox to manage internet contents such as Adobe Flash, Adobe Reader, Windows Media Player, Java, Quicktime, Silverlight etc., and perhaps, there were some other plug-ins also installed automatically and those were actually not required for our work. So, these type of (unwanted) plug-ins could make slowing the speed of Firefox and they can be rectified by disabling them.
Managing plugins: Click the Firefox button and select Add-ons from the drop-down menu. (or from Menu bar > Tools > Add-ons)
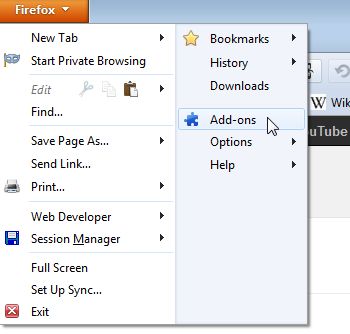 Now Add-ons Manager will open in a new tab. Click 'Plugins' from the
left side of the tab. A list of installed plug-ins will be displayed. For the plugin(s) that you want to disable, click the
corresponding 'Disable' button at the right.
Now Add-ons Manager will open in a new tab. Click 'Plugins' from the
left side of the tab. A list of installed plug-ins will be displayed. For the plugin(s) that you want to disable, click the
corresponding 'Disable' button at the right.
NOTE: Plugins can only be disabled and they can not be deleted or uninstalled; but the plugin is associated with an extension, then the plugin could automatically be removed while uninstalling the extension.
After disabling, the plug-ins went gray in color and Disable button changes to Enable and it can be changed again to Disable, if required.
Aware when disabling plug-ins such as Flash Player, QuickTime, and Java Applets etc., that were often take part in lots of web site to run the applications, videos etc.,
As indicated earlier, plugins can not be uninstalled, manually. Most plugins, however, come with their own un-installation utilities. Visit plugins article from Firefox Help site for the information how to uninstall various common plugins. Further if you find an uninstaller program doesn't work for a particular plugin, then visit manually uninstall a plugin.

Extension is a programming file that serves
to extend the capabilities or the data available to a basic program.
It is a kind of (or list of) commands which are directly included in the
program. This term often (mistakenly) coincides with plug-in.
When installing software, you may be instructed to take one or more
steps related to installing extensions (or these steps may automatically
be done for you).
In Firefox, extensions are doing a roll to add additional functions
such as blocking advertisements, downloading videos, integrating social
network sites etc., and enhancing the features of Firefox, too.
However, installing more extensions will slowing down the speed of Firefox. So, installing less (or required) extensions will keep Firefox speed normal. To speeding up Firefox, extensions should be disabled (not to be uninstalled) and later those can be enabled due to our requirements.
To disable an extension click 'Extensions' from the left side of Add-ons Manager.
The extension is also changed to grey color when it will be disabled. And the same could also be enabled, if required. Some extensions are incompatible with the newer version of Firefox and could not be work.
Most
extensions require you to restart Firefox to be disabled. If you get a
restart message, as shown in the below image, then click 'Restart now'
link.
Note: Option button is not available for disabled extensions and
the disabled extensions are moved to the end of the extensions list.
If you like to remove an extension, completely, then open Add-ons Manager and search the extension that you want to remove from the list. Click the Remove button corresponding to the extension. If you get Restart message for removed extension, then click Restart now link to complete the removal process.
Note: An extension can also be removed, when it is in disabled mode.
Browsing Data: Firefox also keeps the tracks of sites that you've visited as files downloaded, cookies, and more. All these data were collected in the history and when the history database became larger and larger then Firefox will be slowing down or crashing. Firefox provides several methods to clear the browsing data.
From Menu bar click History then select Clear Recent History from the drop-down menu.

From 'Clear All History' dialog box (as pictured below), you can choose the deletion type as you wish. Select the boxes under 'Details' for the items you want to clear.
Note: If you choose 'Everything', a warning message will display and saying 'This action cannot be undone'.
Clear Browsing Data for a Single Website: If you like to keep browsing data for few websites, and not for others then you may choose selected data for the specific sites to clear browsing history. From Menu bar click History then select Show All History from the drop-down menu.
The Library dialog box will display. From left pane of Library dialog box, choose the time frame (i.e.,Today, Yesterday and so on) that you visited the websites, and to clear the history.
A list of websites, for the time you visited, will be displayed in the right pane (as shown above). Right click on the desired website in the list and select 'Forget About This Site' from the popup menu. If there will be a long list of sites, you can use 'Search History' box to find out the desired website.
Note: Firefox doesn't provide re-confirmation message for this process while you delete the desired sites.
Clear Browsing Data When Firefox Exits: To clear browsing data, automatically, when you close Firefox, from Menu bar choose Tools > Options.
From Options dialog box, open 'Privacy' tab and select 'Use custom settings for history' under 'History' section.
Now you'll be prompted for additional options as shown in the below picture. Tick the box of 'Clear history when Firefox
closes' then click 'Settings' button.

Now 'Settings for Clearing History' dialog box will be opened; tick the boxes for the items that you want to clear when you close Firefox then click OK button. You'll be taken, again, to the 'Options' dialog box; click OK to accept your changes.

!!!HAPPY SPEEDY BROWSING!!!
Visit For CHROME: Happy Speedy Browsing - CHROME!